
Flap and skin
Consultation
Flap and skin
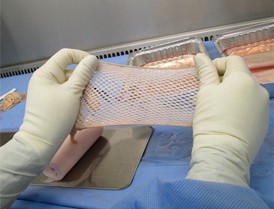
Skin Grafting
Definition
Skin grafting involves taking a piece of skin from one area of the body (donor site) and transplanting it to another area (recipient site).
Types of Skin Grafts
Full-Thickness Grafts: Involving the entire thickness of the skin, including the epidermis and dermis, usually taken from areas with excess skin, such as the buttocks or upper arm.
Split-Thickness Grafts: Involving only a portion of the dermis, often taken from the thigh or buttock. These grafts are more commonly used because they cover larger areas.
Procedure
The donor skin is harvested and carefully placed on the recipient site. The graft is then secured with stitches, staples, or a dressing to promote healing.
Indications
Skin grafts are suitable for covering large wounds, burns, or areas where tissue loss has occurred. They are commonly used in reconstructive surgery after tumor removal or trauma.
Healing Process
The success of a skin graft relies on the graft developing new blood vessels (vascularization) and integrating with the surrounding tissues.
Complications
Possible complications include graft failure, infection, or differences in color and texture between the grafted skin and the surrounding tissue.
Flap Surgery
Definition:
Flap surgery involves transferring a section of skin along with underlying tissue (muscle, fat, or blood vessels) from one part of the body (donor site) to another (recipient site).
Types of Flaps
Local Flaps: Tissue is moved from an adjacent area to cover the defect.
Regional Flaps: Tissue is taken from a nearby region with a blood supply, often involving muscle or fascia.
Free Flaps: Tissue is detached from its blood supply, moved to the recipient site, and reconnected with blood vessels.
Procedure
The flap is dissected, transferred to the recipient site, and revascularized by connecting blood vessels. The donor site may require its own closure or reconstruction.
Indications
Flap surgery is used for more complex reconstructions, such as in cases of large defects, complex wounds, or when a significant amount of tissue is needed.
Healing Process
Flap surgery provides a robust blood supply, enhancing the chance of successful healing. The flap gradually integrates with the surrounding tissues.
Complications
Complications may include partial or total flap loss, infection, or issues with blood supply.
Considerations
Choosing Between Grafts and Flaps
The choice between skin grafts and flap surgery depends on factors such as the size and location of the defect, the available donor sites, and the specific needs of the patient.
Recovery
Recovery varies depending on the type and complexity of the procedure. Both grafts and flaps may require careful postoperative care and monitoring.
Consultation
A thorough consultation with a plastic surgeon is crucial to determine the most appropriate technique based on the individual’s condition and desired outcomes.
Skin grafting and flap surgery are valuable tools in the field of reconstructive surgery, allowing surgeons to restore form and function to areas affected by trauma or medical conditions. The choice between these techniques depends on the specific requirements of each case, and a skilled surgeon will tailor the approach to meet the unique needs of the patient.

