
Post-burn
Consultation
Post-burn
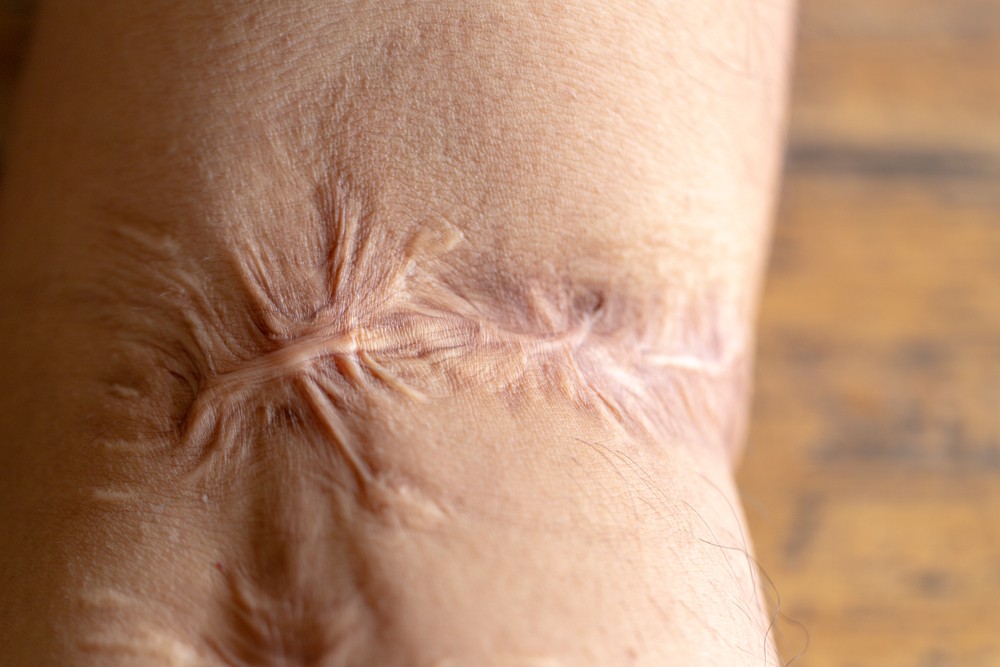
Causes of Post-Burn Contractures
Scar Tissue Formation
After a burn injury, the body initiates the healing process by forming scar tissue. In some cases, excessive or hypertrophic scarring can lead to contractures.
Deeper Burns
Deeper burns, such as second-degree or third-degree burns, are more likely to result in post-burn contractures.
Lack of Proper Treatment
Inadequate wound care, delayed medical treatment, or insufficient rehabilitation after a burn injury can contribute to the development of contractures.
Location of Burn
Burns that occur over joints or areas prone to movement are more likely to lead to contractures.Areas of Post-burn contractures Neck:
Burns to the neck can lead to contractures that restrict head movement and affect the ability to tilt or turn the head.
Axilla (Underarm)
Burns in the axillary region can result in contractures that limit the movement of the arm and shoulder.
Burns to the neck can lead to contractures that restrict head movement and affect the ability to tilt or turn the head.
Elbow
Burn injuries over the elbow joint may lead to contractures, restricting the extension or flexion of the arm.
Wrist and Hand
Burns on the wrist and hand can cause contractures that affect finger movement, grip strength, and overall hand function.
Chest
Burns on the chest area can lead to contractures that restrict chest expansion, impacting breathing and lung function.
Abdomen
Burns on the abdomen may result in contractures that limit trunk movement and flexibility.
Hip
Hip contractures can occur following burns in the hip region, affecting the ability to move the leg and pelvis.
Knee
Burns around the knee joint can lead to contractures that restrict the bending or straightening of the knee.
Ankle and Foot
Burns on the ankle and foot may cause contractures affecting walking, balance, and overall lower limb function.
Face
Burns on the face, particularly around the mouth and eyes, can result in contractures that impact facial expressions, eye closure, and mouth movement.
Fingers and Toes
Burn injuries on the digits (fingers and toes) can lead to contractures affecting the range of motion and functionality of the digits.
Signs and Symptoms:
Limited Range of Motion
The affected joint or area may have restricted movement.
Tightness and Stiffness
The skin and tissues around the scarred area may feel tight and stiff.
Deformities
Contractures can result in deformities, altering the normal shape and appearance of the affected body part.
Pain and Discomfort
Some individuals may experience pain or discomfort when trying to move the affected area.
Treatment and Management
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a key component of managing post-burn contractures. Therapists work with patients to improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and prevent further contracture development.
Splinting and Stretching
Splints and stretching exercises are commonly used to maintain or restore joint flexibility and prevent contractures.
Scar Management
Techniques such as massage, silicone sheets, and topical treatments may be used to manage scar tissue and prevent excessive scarring.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists can assist individuals in adapting to activities of daily living and using assistive devices if needed.
Surgical Intervention
In cases of severe contractures that do not respond to conservative measures, surgical intervention may be considered. This may involve releasing or excising scar tissue and reconstructing the affected area.
Preventive Measures
Early and appropriate wound care, prompt medical treatment, and ongoing rehabilitation are crucial in preventing the development of post-burn contractures.
Prevention
Early Mobilization
Encourage early movement and mobilization of joints to prevent stiffness and contractures.
Wound Care
Proper wound care and management of the burn injury can reduce the risk of excessive scarring.
Regular Follow-Up
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers for assessment and intervention can help identify and address contractures early.
Compliance with Treatment Plans
Adhering to recommended treatment plans, including physical therapy and scar management, is essential.
Post-burn contractures can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. Early intervention, proper wound care, and ongoing rehabilitation are crucial in preventing and managing these complications. A multidisciplinary approach involving burn specialists, physical therapists, and occupational therapists is often necessary to optimize outcomes for individuals with post-burn contractures.

