
Varicose veins
Consultation
Varicose veins
Causes of Varicose Veins
Faulty Valve Function
Varicose veins often develop when the valves in the veins that help blood flow toward the heart become weak or damaged. This leads to the pooling of blood in the veins.
Heredity
A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing them.
Age
The risk of varicose veins increases with age as the veins lose elasticity and valves weaken.
Gender
Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men, particularly during pregnancy due to increased pressure on the veins.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Jobs or activities that involve long periods of standing or sitting may contribute to the development of varicose veins.
Obesity
Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Symptoms
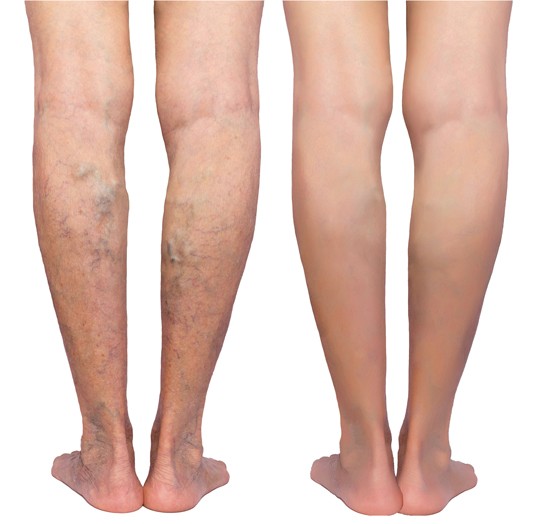
Visible, Bulging Veins
Varicose veins are often visible beneath the skin, appearing swollen, twisted, and discolored.
Aching or Pain
Individuals with varicose veins may experience aching or pain in the legs, especially after standing for long periods.
Heaviness or Fatigue
The affected legs may feel heavy, tired, or restless.
Swelling
Swelling, particularly around the ankles, may occur.
Itching or Burning
Some individuals may experience itching or a burning sensation around the veins.
Skin Changes
Over time, skin around the affected veins may become discolored or develop sores (in severe cases).
Treatment and Management:
Lifestyle Changes
Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting can help manage varicose veins.
Compression Stockings
Compression stockings provide support to the veins and help improve blood circulation.
Elevation
Elevating the legs when resting can reduce swelling and discomfort.
Sclerotherapy
This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting a solution into the vein, causing it to collapse and eventually fade.
Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
A laser is used to heat and close the affected vein, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Similar to EVLA, this procedure uses radiofrequency energy to close off the varicose vein.
Vein Stripping and Ligation
In more severe cases, the affected vein may be surgically removed or tied off.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
Small incisions are made to remove segments of the affected vein.
It’s important to note that while treatments can improve the appearance of varicose veins and alleviate symptoms, they may not prevent the development of new varicose veins in the future. If you’re experiencing symptoms of varicose veins, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a vascular specialist who can assess your condition and recommend an appropriate course of action.

